Introduction To Accounting
The Accounting Equation
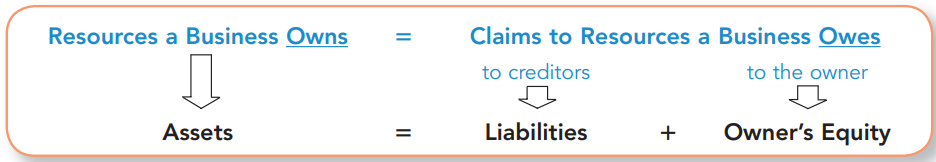 This can be extended to show the effects of revenues, expenses, and owner investments and withdrawals.
This can be extended to show the effects of revenues, expenses, and owner investments and withdrawals.
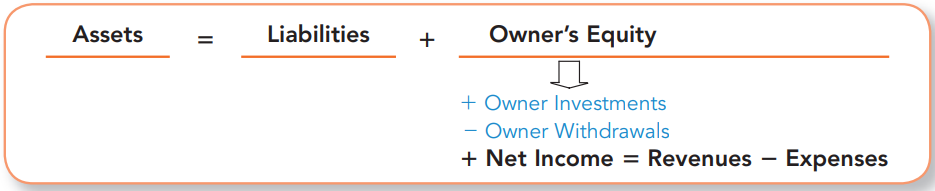
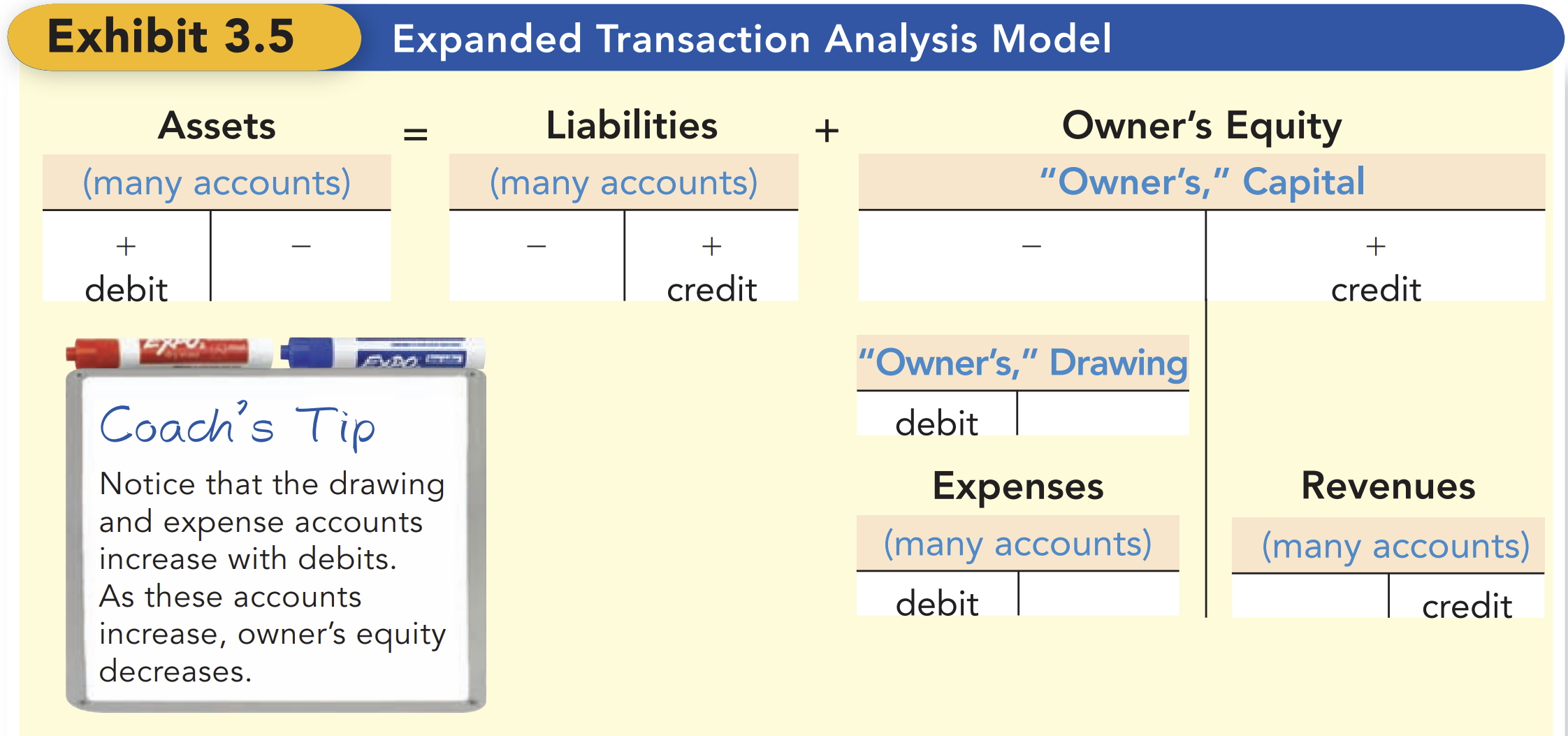 To increase an expense, then you debit it.
To increase an expense, then you debit it.
The Account Titles
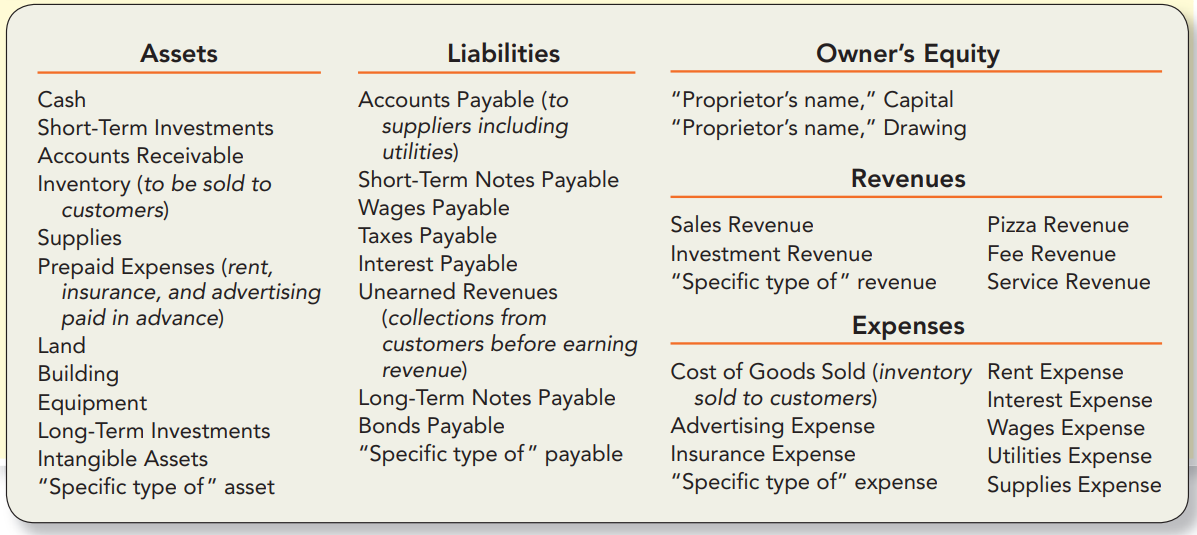
- “Receivables” are assets.
- “Payables” are liabilities.
- A prepaid expense account is always an asset.
- An unearned revenue account is always a liability.
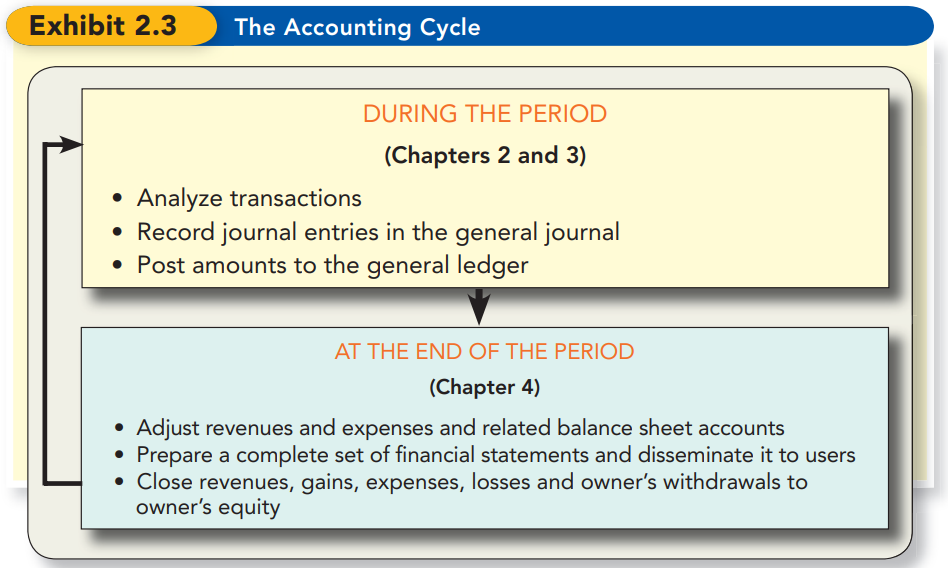
The Accounting Cycle
Transaction Analysis
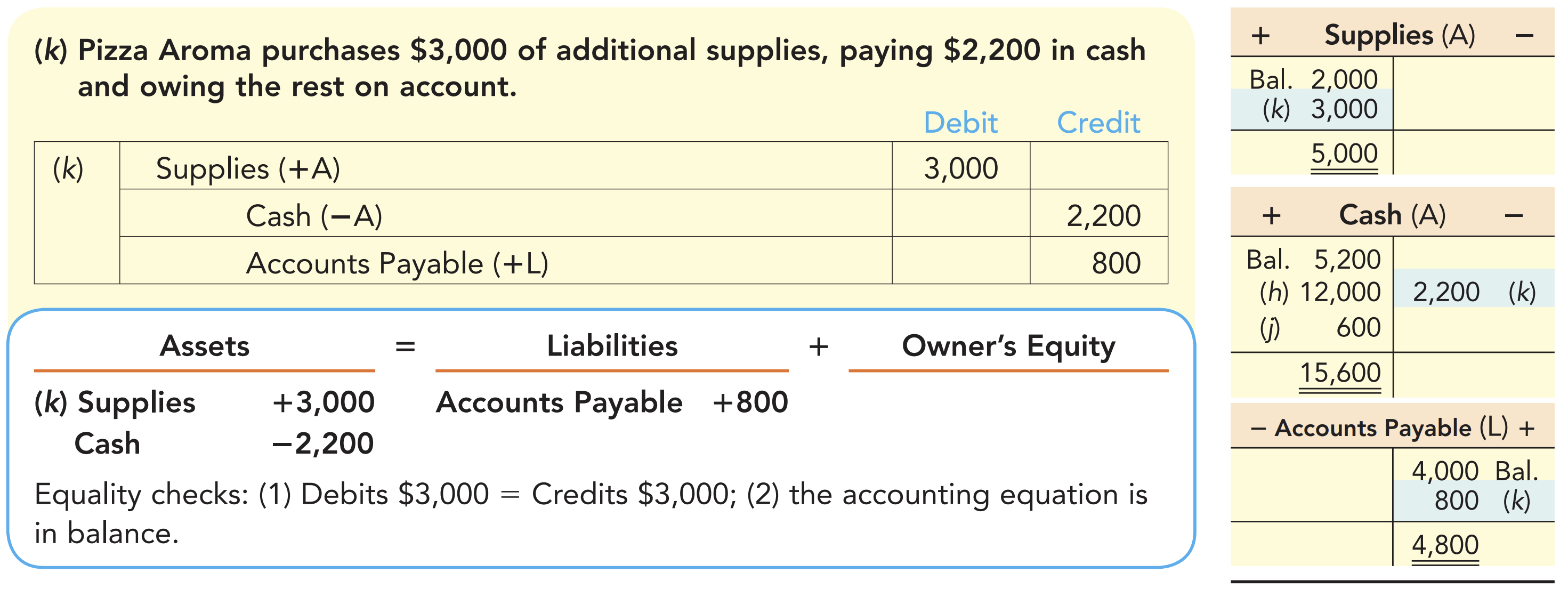
There are two rules to follow:
- Dual effect: Every transaction affects at least two accounts.
- Balancing the accounting equation: The accounting equation must remain in balance after each transaction is recorded.
Here’s one example.
In accrual basis accounting, revenues are recognized when they are earned and expenses are recognized when they are incurred.
Revenue Part
- The key to determining when to report revenue is whether the business has done what it promised to do.
- Following the revenue principle, a business records revenue when it delivers goods or services, not when it receives cash.
General journal & General ledger
There’re two types of records or books in a bookkeeping system.
- General journal
- General ledger, in which each page represents a separate account.